 You can see some really neat things in the night sky this October: planets, shooting stars, and some rare, eery morning light called the “False Dawn”! You can use the Moon to find many of the interesting sights overhead this month, including Saturn. In fact, Saturn is getting lower and lower in the sky, and October will be the last chance to get a good view of Saturn in 2016.
You can see some really neat things in the night sky this October: planets, shooting stars, and some rare, eery morning light called the “False Dawn”! You can use the Moon to find many of the interesting sights overhead this month, including Saturn. In fact, Saturn is getting lower and lower in the sky, and October will be the last chance to get a good view of Saturn in 2016.
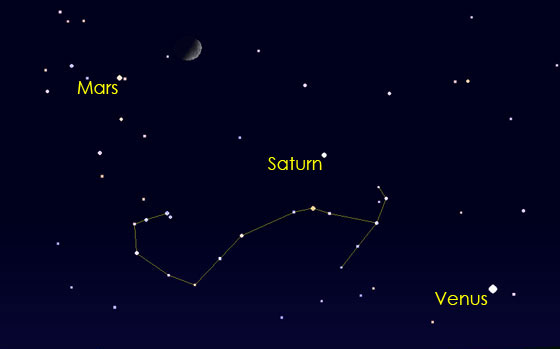
October 3 — Look for Venus near the thin, crescent Moon over your western horizon near sunset. Venus will be the brightest point of light low on the horizon, near the Moon.
October 5 & 6 — The Moon will appear near the beautiful, ringed planet Saturn, which will be hovering near the constellation Scorpius.
October 7 & 8 — The Moon will appear near the red planet Mars.
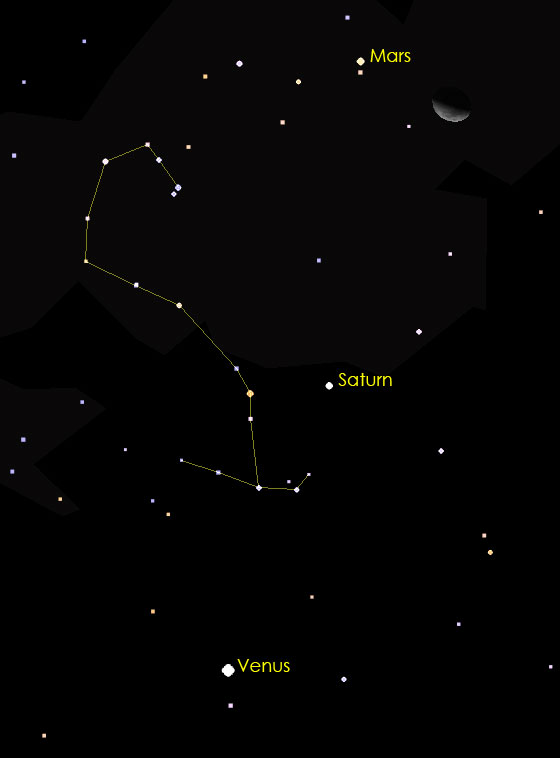

On October 15 the planet Uranus will reach its maximum brightness for the year. So pull out your telescope and take a peek! Uranus will be easy to spot as it will appear next to the Moon that night. Through a telescope it will appear as either a grey circle or a faint green dot, depending on whether you have a small or large telescope, respectively.

If you’re an early bird, you can use the Moon in the pre-dawn skies to see a couple of beautiful sites in October. On October 19 the Moon will be near the “Hyades” star cluster, which is a V-shaped group of stars in the constellation Taurus. Nearby is another cluster of stars known as the “Pleiades.” Many people confuse the Pleiades with the Little Dipper, which is actually located over the northern horizon. And on October 28, the thin, crescent Moon will appear near Jupiter, the king of the planets, in the east near sunrise.
October’s Shooting Stars

The Orionid meteor shower peaks before dawn on October 21, although you can see its shooting stars from October 2 through November 7. To get the best view, lie down outside with the Moon at your back in the pre-dawn hours. It’s called the “Orionid meteor shower” (a.k.a., “the Orionids”) because the shooting stars all appear to fly out of the constellation Orion. The meteors are leftover dust particles from the many visits of Halley’s Comet every 75 years to our neck of the solar system. Each October, as Earth passes through the dust trail left behind by Halley’s Comet, the meteors burn up in the atmosphere as “shooting stars.” Actually, Halley’s Comet is responsible for two meteor showers each year: the Orionid meteor shower each fall and the “Eta Aquarid” meteor shower each spring.
October’s False Dawn

If you live far from city lights, consider waking up early sometime in the first half of October and look for the “False Dawn” — a beautiful, triangle-shaped glow of cosmic light that appears in the eastern sky before sunrise. See our blog article about “Fall’s False Dawn” for details.
Get our Moon Tweets!

Did you know you can use the Moon to identify where your star’s constellation is in the night sky? Follow us on Twitter where we let you know when the Moon appears in a Name A Star constellation (area of the night sky).
Name A Star Live offers some really good tools to learn about the night sky and find your star’s constellation. Visit our website to learn about our Virtual Planetarium software, planisphere constellation finder, and First Light Astronomy Kit!